Swedens geography and climate
On this page, you can read about how Sweden is divided geographically, about the climate and the different seasons
Summary
- Quota refugees are resettled in all parts of Sweden.
- Sweden is divided into counties, which are grouped into three areas: Norrland, Svealand and Götaland. The nature and climate in the different parts vary.
- Sweden has four seasons, all with different weather.
- You need to change your clothes to suit the different weather and seasons. For example, during the winter you need warm clothes when you are outdoors.
Facts about Sweden
Sweden is located in northern Europe. It is one of the largest countries in Europe, but with only around 10 million inhabitants. The country is 1,600 kilometres long and 500 kilometres wide. The capital of Sweden is Stockholm and the official language is Swedish.
Sweden is located on the Baltic Sea and has its own coastline. Sweden's neighbouring countries are Norway to the west, Denmark to the south and Finland to the east. On the eastern side, Sweden borders the Baltic Sea along the entire length of the country. Sweden has good relations with its neighbouring countries.
A world map with Sweden marked in red. Photo: Swedish Migration Agency/Elin Hägg
Regional differences
Sweden is divided into three parts. The climate and nature vary in the different parts. There are towns and villages in all parts of Sweden but southern and central Sweden have more inhabitants and larger cities.
- Norrland (northern Sweden) has a lot of mountains, forests and lakes. There is not much agricultural land and there are fewer inhabitants here than in the rest of the country. Northern Sweden is known for its natural beauty.
- Svealand (central Sweden) has a lot of forests but also agriculture. Sweden's capital city, Stockholm, is located on the eastern side of central Sweden.
- Götaland (southern Sweden) has a lot of agricultural land and long beaches. The large cities of Göteborg and Malmö are located in southern Sweden.
Quota refugees are resettled in municipalities in all parts of Sweden. Regardless of whether you live in a city or in the countryside, everyone in Sweden has access to education and other services such as healthcare and childcare.
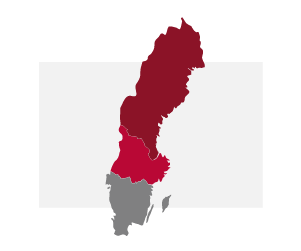
Sweden's three parts: Norrland, Svealand and Götaland. Photo: Swedish Migration Agency/Elin Hägg
Weather and climate
Sweden has four seasons with different weather. Each season has both rain/snow and sun. The differences between the seasons are most noticeable in the temperature, vegetation and amount of daylight.
The weather in the northern parts of Sweden is colder than in the southern parts. In the north, the winters are longer and with more snow. The summers are warm throughout the country. Because Sweden is so far north, the country has many hours of daylight during the summer and very few during the winter. These differences are particularly noticeable in northern Sweden, where you have almost 24 hours of daylight in the middle of summer, and almost none for most of the day during the winter.
Winter
December, January and February.

Winter is the coldest season. The temperature drops and it is often below freezing. It snows, especially in the northern parts of the country where the snow remains longer. Lakes and other bodies of water may freeze. Residents go to school and work as usual even when it is cold and snowy. Most of the snow is cleared away from streets and roads. It may rain during the winter, especially in southern Sweden.
There are many popular outdoor activities and winter sports, such as sledding, ice skating and skiing. At school and preschool, the children are outside regardless of the weather and time of year. Warm clothes protect the body against the cold. Due to the cold climate, residents do spend more time indoors during winter. Homes are well insulated and heated.
It is important to wear warm clothes and dress in several layers when you are outside in winter, to protect the body. Staying outside without warm clothes for a long period in freezing temperatures may be harmful.
You can wear:
- A warm jacket and coveralls (ski-pants) and warm overalls for children.
- A warm hat for your head.
- Gloves for your hands.
- A shawl or scarf.
- Warm socks and shoes/boots.
Spring
March, April and May.
Spring is a time of transition when cold winter turns into warm summer. During spring, the temperature rises, snow and ice melt and vegetation starts to turn green. The days get brighter and longer.
A jacket or coat, scarf, gloves and water-resistant shoes are usually needed outdoors.
Summer
June, July and August.
%20anna_h%C3%A5llams-family_by_the_lake-7260.jpg)
Photo: Anna Hållams/imagebank.sweden.se
Summer is the warmest season of the year. The weather is often warm and sunny and plants are in bloom. Some days, however, can be rainy, cloudy and cool. The days are longer and the evenings are bright.
During the summer, many people engage in outdoor activities and spend time in parks, go swimming and enjoy the warm and sunny weather.
Normally, thinner clothes are enough during the day and you usually do not need to wear a jacket.
Autumn
September, October and November.
%20emelie_asplund-playing_in_the_rain-4326.jpg)
Photo: Emelie Asplund/imagebank.sweden.se
Autumn is a time of transition when warm summer turns into cold winter. The weather is cooler, plants wilt and leaves fall from the trees. The days become shorter and darker. At times, it may be cloudy and rainy. In late autumn, it may start to snow, especially in the northern parts of the country. In southern Sweden, the snow usually melts away quite quickly.
A jacket or coat, scarf, gloves as well as water-resistant shoes are good to have outdoors. However, you do not have to wear your warmest outdoor clothes yet.
Topics to discuss
- How many seasons are there in your home country?
- Do you have warm clothes that you can take with you to Sweden?